Adapted from https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/exceptions/throwing.html
The
throw statement requires a single argument: a throwable object. Throwable objects are instances of any subclass of the Throwable class. Here's an example of a throw statement.throw someThrowableObject; // Note: here is an object
Throwable Class and Its Subclasses
The objects that inherit from theThrowableclass include direct descendants (objects that inherit directly from theThrowableclass) and indirect descendants (objects that inherit from children or grandchildren of theThrowableclass). The figure below illustrates the class hierarchy of theThrowableclass and its most significant subclasses. As you can see,Throwablehas two direct descendants:ErrorandException.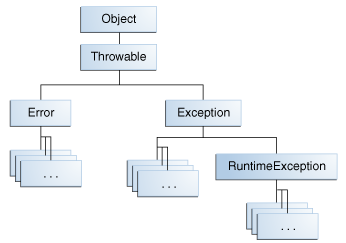 The Throwable class.
The Throwable class.Error Class
When a dynamic linking failure or other hard failure in the Java virtual machine occurs, the virtual machine throws anError. Simple programs typically do not catch or throwErrors.Exception Class
AnExceptionindicates that a problem occurred, but it is not a serious system problem. Most programs you write will throw and catchExceptions as opposed toErrors.The Java platform defines the many descendants of theExceptionclass. These descendants indicate various types of exceptions that can occur. For example,IllegalAccessExceptionsignals that a particular method could not be found, andNegativeArraySizeExceptionindicates that a program attempted to create an array with a negative size.OneExceptionsubclass,RuntimeException, is reserved for exceptions that indicate incorrect use of an API. An example of a runtime exception isNullPointerException, which occurs when a method tries to access a member of an object through anullreference.
A program can use exceptions to indicate that an error occurred. To throw an exception, use thethrowstatement and provide it with an exception object — a descendant ofThrowable— to provide information about the specific error that occurred. A method that throws an uncaught, checked exception must include athrowsclause in its declaration.A program can catch exceptions by using a combination of thetry,catch, andfinallyblocks.
- The
tryblock identifies a block of code in which an exception can occur.- The
catchblock identifies a block of code, known as an exception handler, that can handle a particular type of exception.- The
finallyblock identifies a block of code that is guaranteed to execute, and is the right place to close files, recover resources, and otherwise clean up after the code enclosed in thetryblock.Thetrystatement should contain at least onecatchblock or afinallyblock and may have multiplecatchblocks.The class of the exception object indicates the type of exception thrown. The exception object can contain further information about the error, including an error message. With exception chaining, an exception can point to the exception that caused it, which can in turn point to the exception that caused it, and so on.
No comments:
Post a Comment